Treatment of Gums
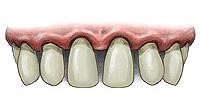
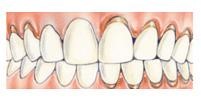
There are Two Stages of gum diseade, Gingivitis and Periodontal.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums surrounding the teeth. Gingivitis is one of many periodontal diseases that affect the health of the periodontium (those tissues that surround the teeth and include the gums, soft tissues, and bone). Chronic gingivitis leads to receding gums and can cause permanent damage to teeth. Gingivitis is a common cause of gum disease and a form of periodontitis.
Periodontal diseases are often classified according to their severity. They range from mild gingivitis, to more severe periodontitis, and more uncommon but serious acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, which can be life-threatening..
Periodontal
Periodontal disease is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth. Teeth are supported by the gums, or gingiva. A tooth’s root is anchored to its socket by fibers called periodontal ligaments.
The gums do not attach to the teeth as firmly as one might think. A shallow, V-shaped gap called a sulcus exists between the teeth and the gums. Periodontal disease affects this gap. Eventually, in periodontal disease, the tissues supporting the tooth break down. If only the gums are involved in this breakdown, the disease is called gingivitis. If only the connecting tissues and bone are involved, it is called periodontitis.